江苏科技信息 ›› 2019, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (1): 52-57.doi: 10.1004-7530/2019-36-1-52
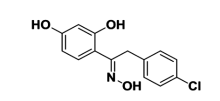
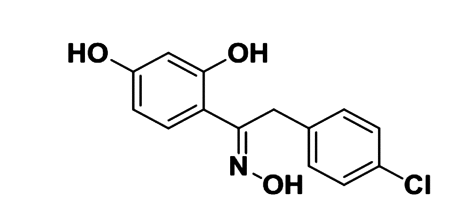
(E)-2-(4-氯苯基)-1-(2,4-2羟基苯)乙酰基肟改善大鼠急性痛风性关节炎的分子机制研究
王毅兵1,彭霁2,*
- 1. 江苏医药职业学院,江苏 盐城 224005
2. 盐城协和医院,江苏 盐城 224005
Study on molecular mechanisms by which (E)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl) ethanone oxime improved acute gouty arthritis in rats
Yibing Wang1,Ji Peng2,*
- 1. Jiangsu Vocational College of Medicine, Yancheng 224005, China
2. Yancheng Xiehe Hospital, Yancheng 224005, China
摘要:
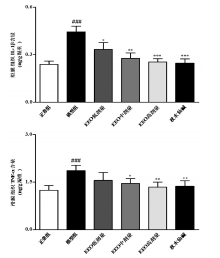
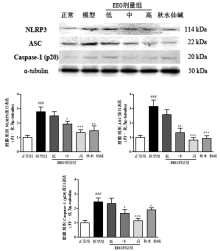
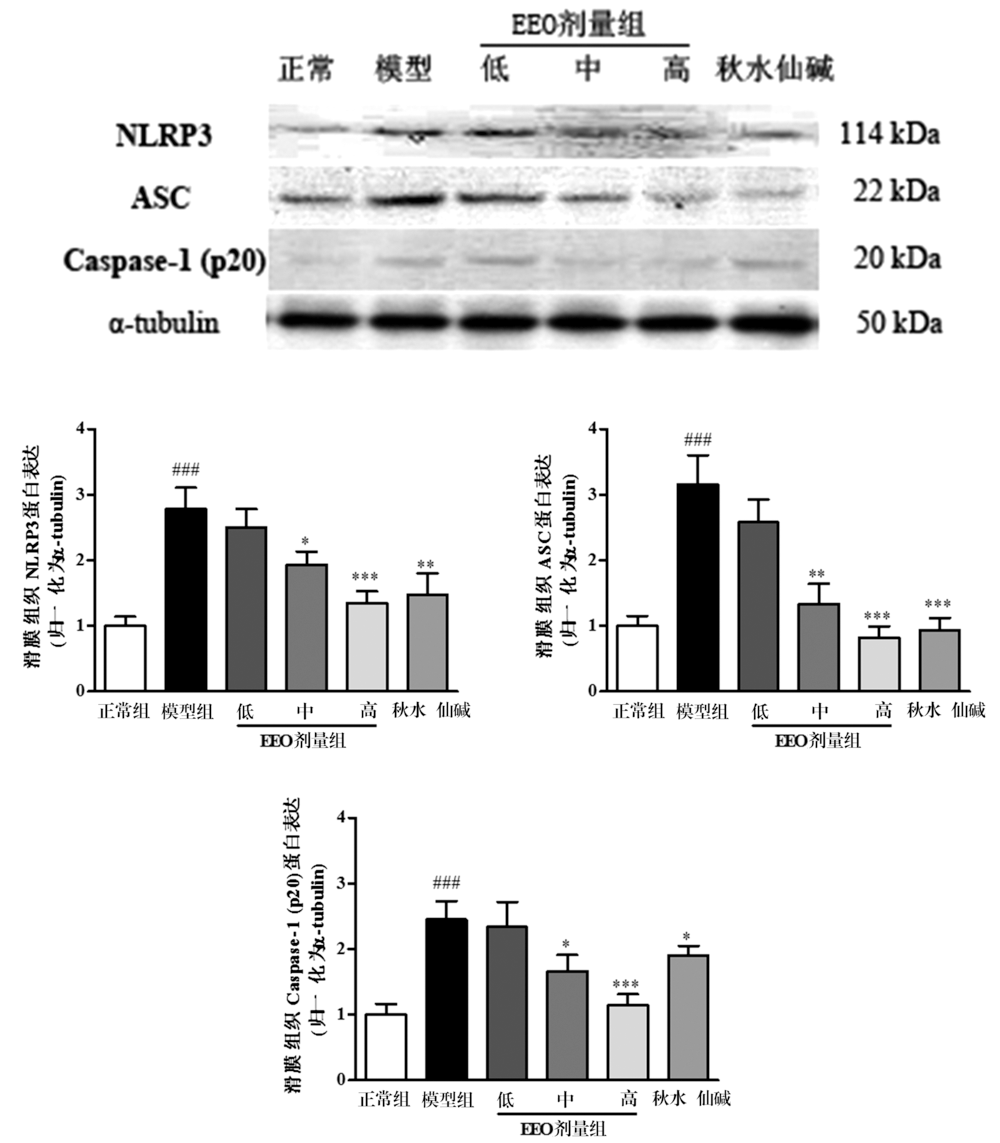
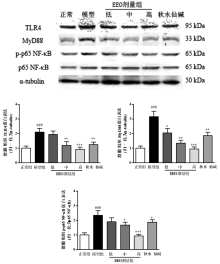
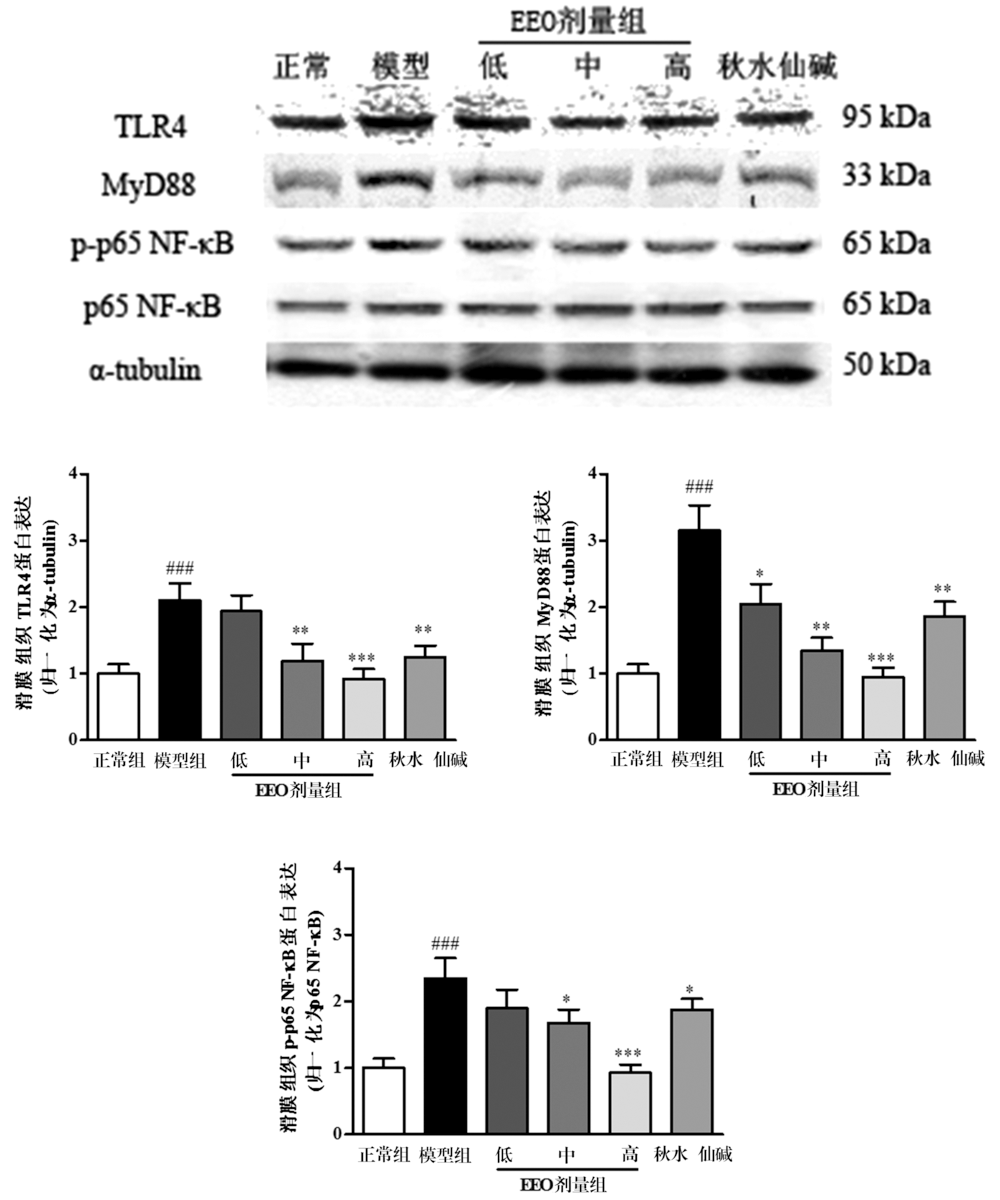
目的:探讨(E)-2-(4-氯苯基)-1-(2,4-2羟基苯)乙酰基肟(EEO)对急性痛风性关节炎的改善作用及其分子机制。方法:随机将大鼠分为正常组、模型组、EEO各剂量组(低、中、高)、秋水仙碱组,各组分别用相应药物灌胃3 d。第3天给药1 h后向大鼠踝关节腔注入尿酸钠晶体(MSU),观察大鼠关节肿胀度变化。24 h后取滑膜组织,ELISA检测组织中白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α的水平,蛋白质印迹检测组织中NLRP3炎性小体各组分和TLR4信号通路关键分子的蛋白表达。结果:与正常组比较,模型组关节周径及滑膜组织中IL-1β和TNF-α的含量显著升高,滑膜组织NLRP3,ASC,Caspase-1,TLR4,MyD88的表达和p65 NF-κB的磷酸化水平显著上调,上述异常均能够被EEO和秋水仙碱逆转。结论:EEO通过调节NLRP3炎症小体和TLR4信号通路缓解MSU诱导的急性痛风性关节炎。
中图分类号: